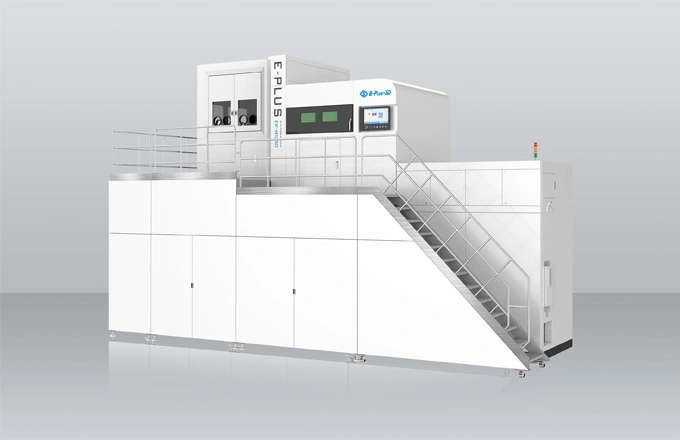
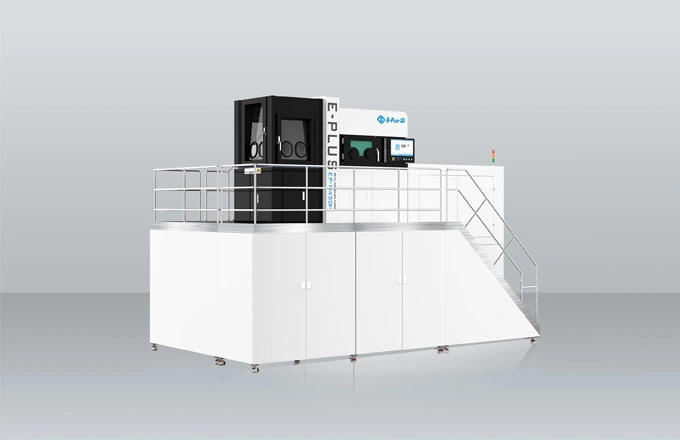
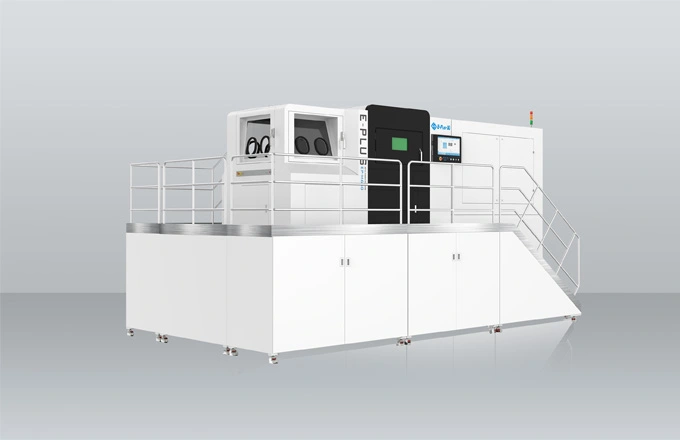
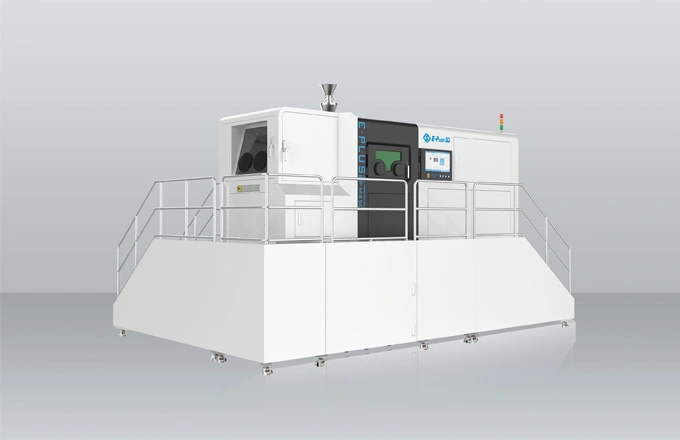
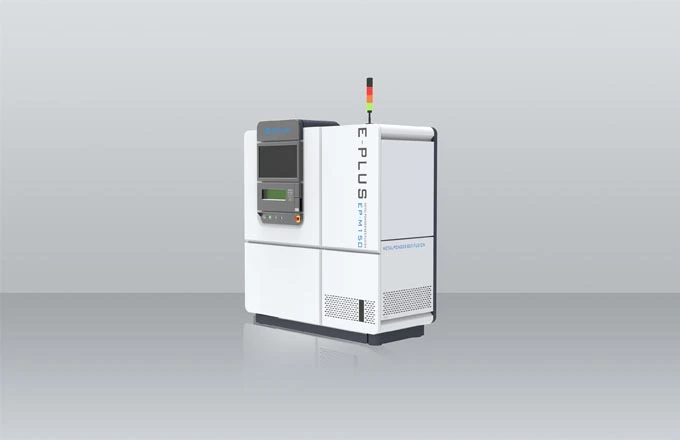
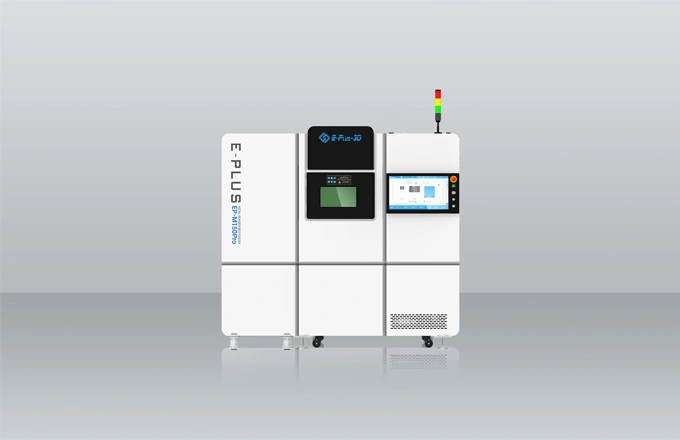
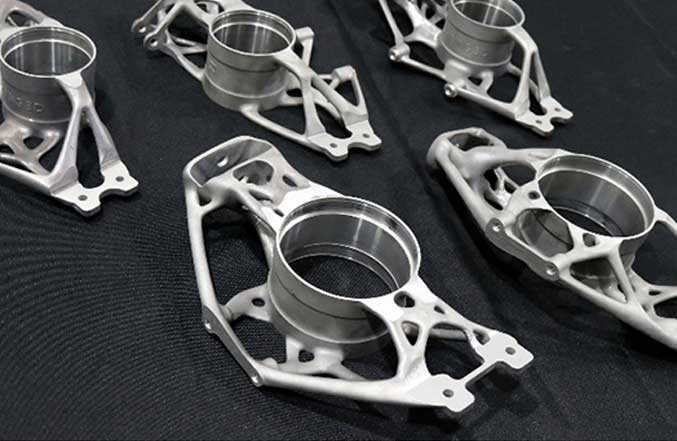
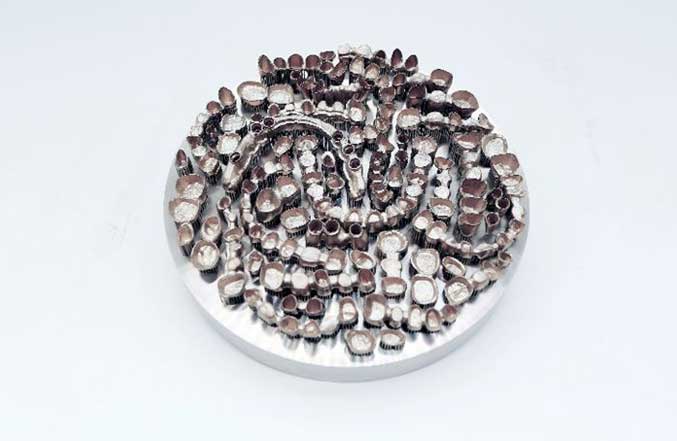
Since the 1990s, 3D printing technology (additive manufacturing) has been applied more and more widely, and the medical industry is a typical example. It is one of the fastest growing industries with 3D printing with a lot of applications, from customized implants to functional prototypes and advanced medical tools.

Applications in the medical field can be served as a typical example of how 3D printing technology used in various industries. We will learn about the current applications of 3D printing in the medical field and the expected development direction of the technology.
Maximizing cost effectiveness in producing customized products is one of the key factors behind the uptake in 3D printing within the medical sector. Due to exerting the design imagination to the maximum and the ability to produce highly complex parts and components, 3D Printing provides an ideal solution to meet the specific needs of the medical industry, and it is changing medical devices from traditional manufacturing way to the new additive manufacturing way.
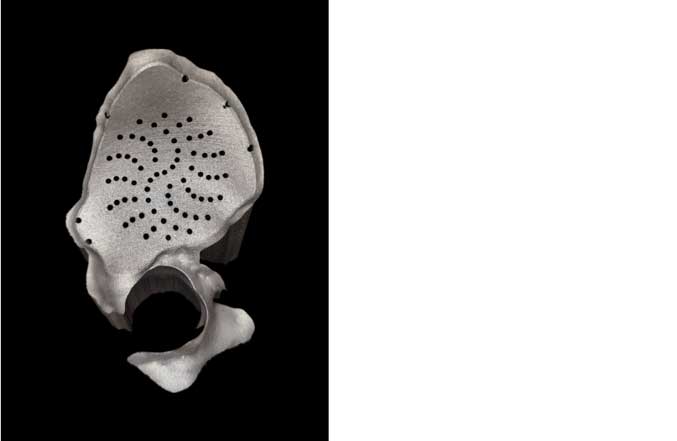
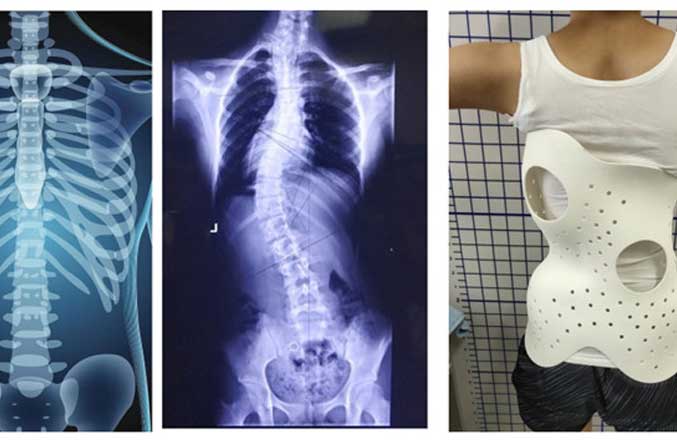
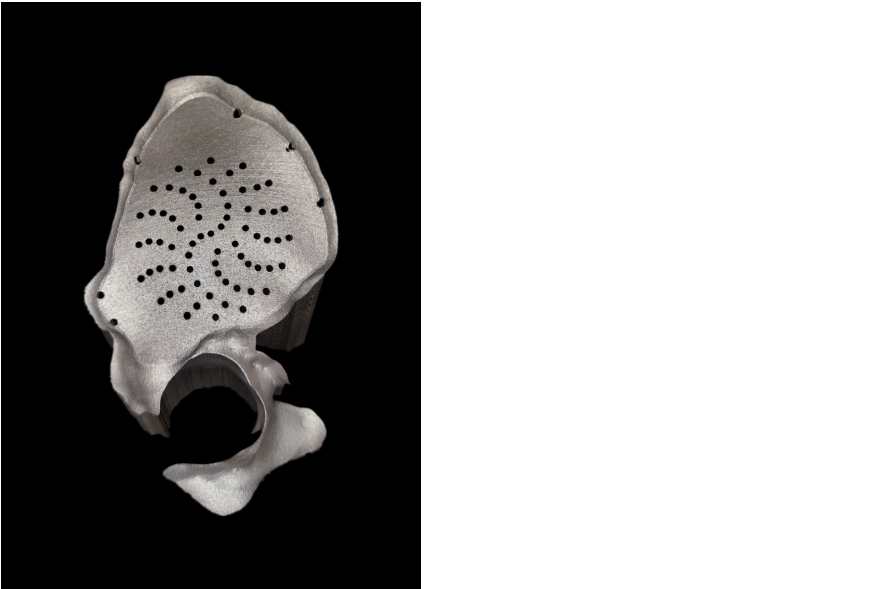
Since each patient is a unique subject, the medical products such as complex-shaped implants, personalized prosthetics and hearing aids, must be tailored to the patient. 3D printing perfectly meets this particular requirement. It simplifies the design of special products and speeds up the manufacturing process.
An obvious disadvantage of using traditional techniques to produce complex medical devices is time-consuming and costly, and it requires expensive production equipment. With advances in 3D printing, it is now much more cost-effective to produce complex medical devices. 3D Printing does not require any mould or specific tools that normally are needed for traditional manufacturing methods. With this technology, we have the ability to make complex devices that can’t be produced by traditional manufacturing ways.
3D printing can significantly improve the fault tolerance of design and the production speed of parts. If a medical device requires any design iterations, it can be iterated with different variations without leading to cost increases or productivity losses. It can also reduce time-to-market for new medical devices.
Early years, because of the lack of 3D authenticity of digital images, doctors can't simulate patients to evaluate complex pathological anatomy directly. But now, with advances in 3D printing, this problem is solved. It also increases the ability to create a model composed of different materials. With this application, this model will replicate the features of human tissue and bone. This method can help surgeons plan an operation in advance, and improve surgical precision and postoperative outcomes.
Dentistry is a mature medical industry for 3D printing. Dental labs can additively manufacture bridges, aligners, crowns, orthodontic appliances and stone models, which can be customized to fit the patient.
With advances in 3D printing, it is sure to emerge many more potential applications. Not just of existing technologies and materials but as new medical specific technologies are designed and developed, 3D printing will continue to change the appearance of the medical industry.