Hangzhou, China - July 2025 - INNOSPACE, global leader in hybrid rocket technology, is leveraging metal additive manufacturing to transform the production of launch vehicle components. By adopting Eplus3D’s MPBF technology and deploying metal 3D printers, INNOSPACE has established an advanced in-house manufacturing system. This marks a key step toward serial production, with 13 core components for the HANBIT rocket already delivered. INNOSPACE conforms to ISO/ASTM 52941-20—the international standard specifying acceptance criteria for metal additive manufacturing equipment used in aerospace—enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and advancing toward scalable, high-reliability launch services.
Who is INNOSPACE?
INNOSPACE is Korea’s private launch vehicle company with proprietary rocket engine technology and a world leader in hybrid rocket systems. The company operates from a localized R&D and manufacturing base in Korea while expanding its global launch network - including a key partnership with Brazil's Alcântara Space Center, where it successfully validated its 15-ton-thrust hybrid rocket engine through the test launch of HANBIT-TLV. To further strengthen its global capabilities, INNOSPACE has also partnered with Equatorial Launch Australia (ELA).
In February 2025, the company successfully obtained AS9100 Aerospace Quality Management Certification from BSI, strengthening its commitment to aerospace-grade quality standards.
Why Adopt Metal Additive Manufacturing?
INNOSPACE is committed to breaking through the gridlocked and costly small satellite launch service market by providing easy, fast, affordable, and reliable access to space. As aerospace components increasingly demand lightweight structures, high-temperature resistance, and precision manufacturing, traditional production methods are falling behind in meeting the needs for rapid iteration and cost efficiency. Meanwhile, the global surge in small satellite launches continues to raise expectations for manufacturing flexibility and productivity. To address these challenges, INNOSPACE has adopted Metal Powder Bed Fusion (MPBF) technology as its core additive manufacturing solution.
“By applying 3D printing technology, we expect to achieve part lightweighting that reduces rocket mass and increases payload capacity, allowing customers to transport more satellites at a lower cost. This will positively impact future revenue generation.” said Soojong Kim, founder and CEO of INNOSPACE.
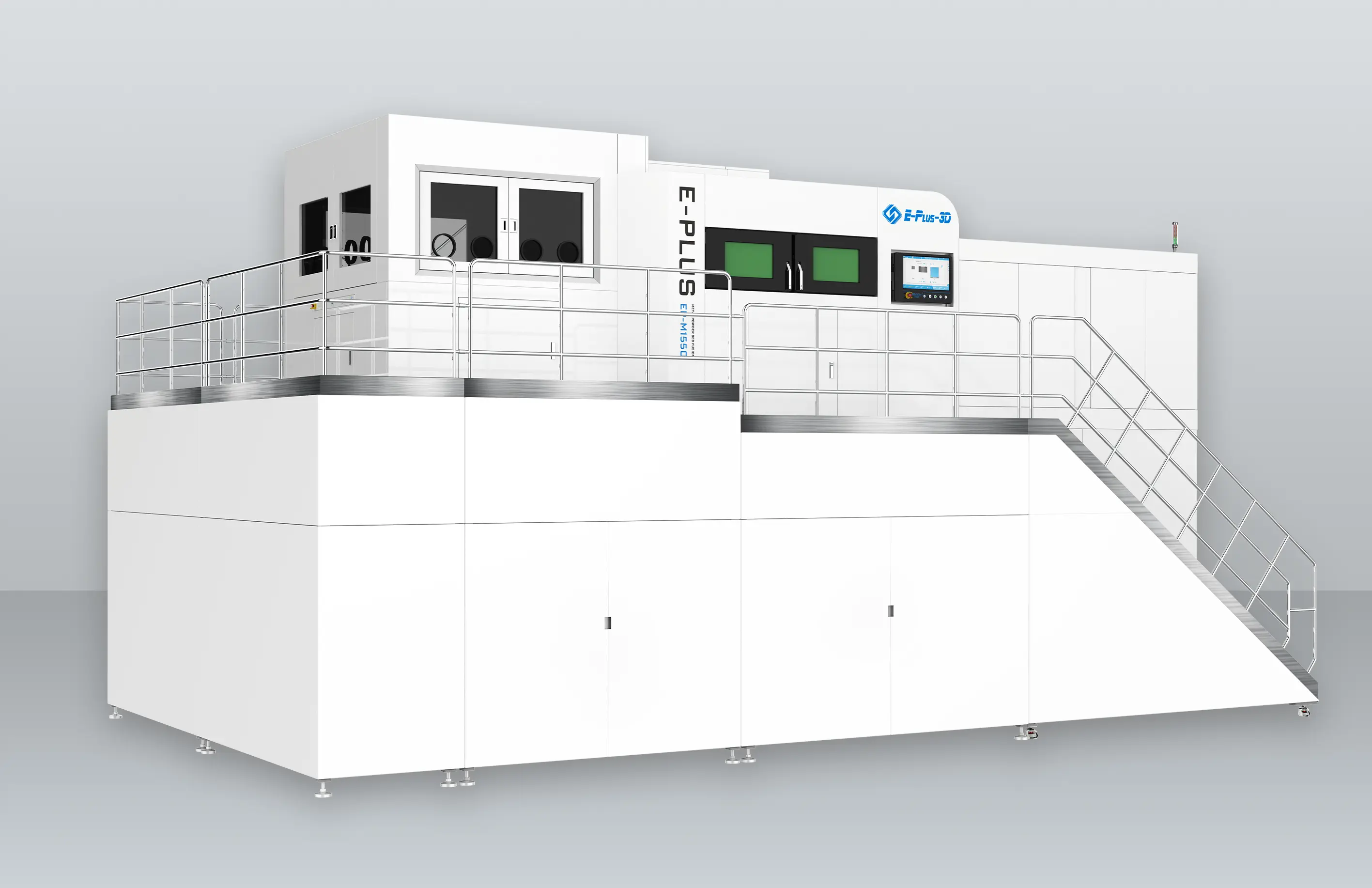
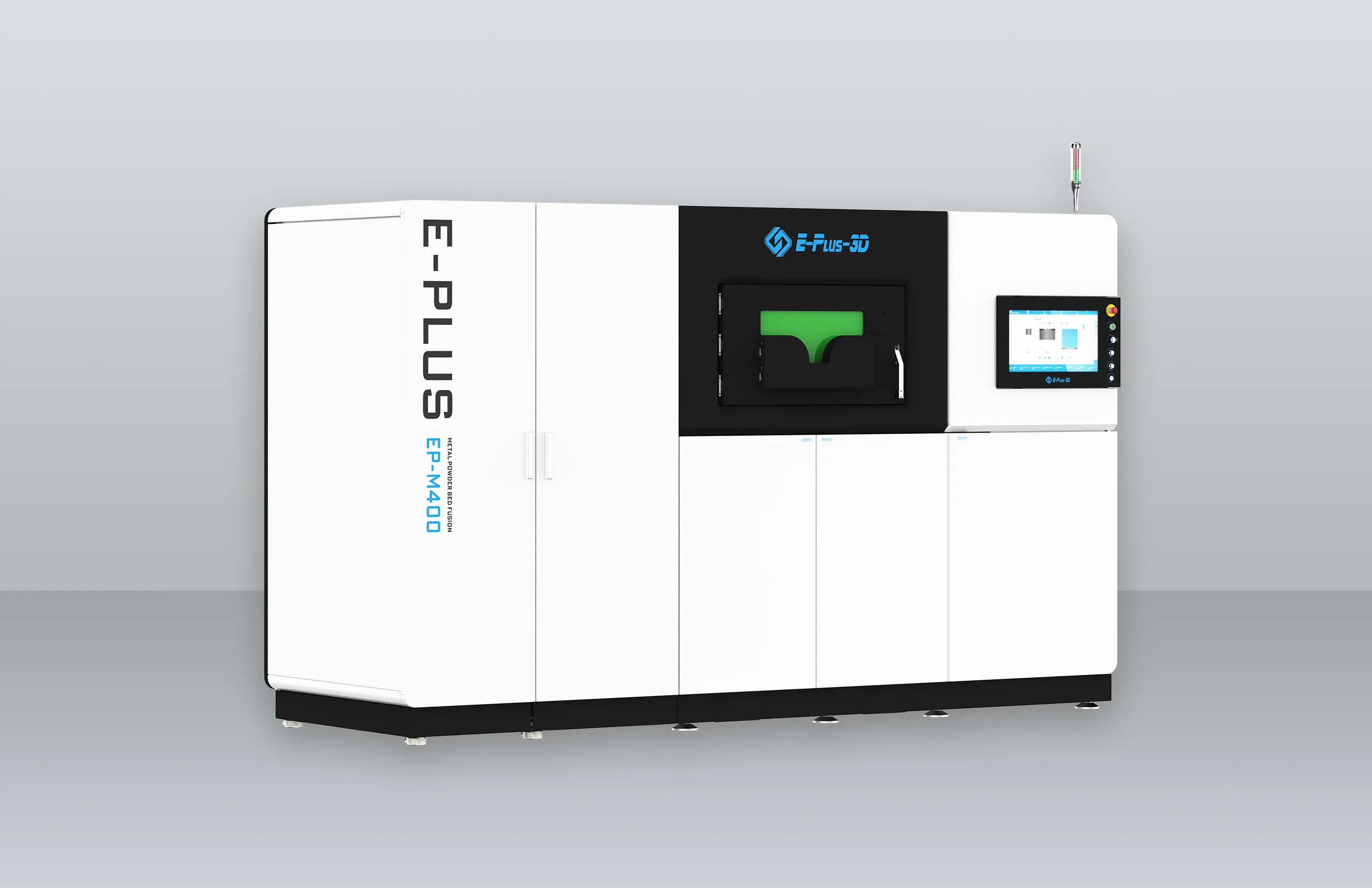
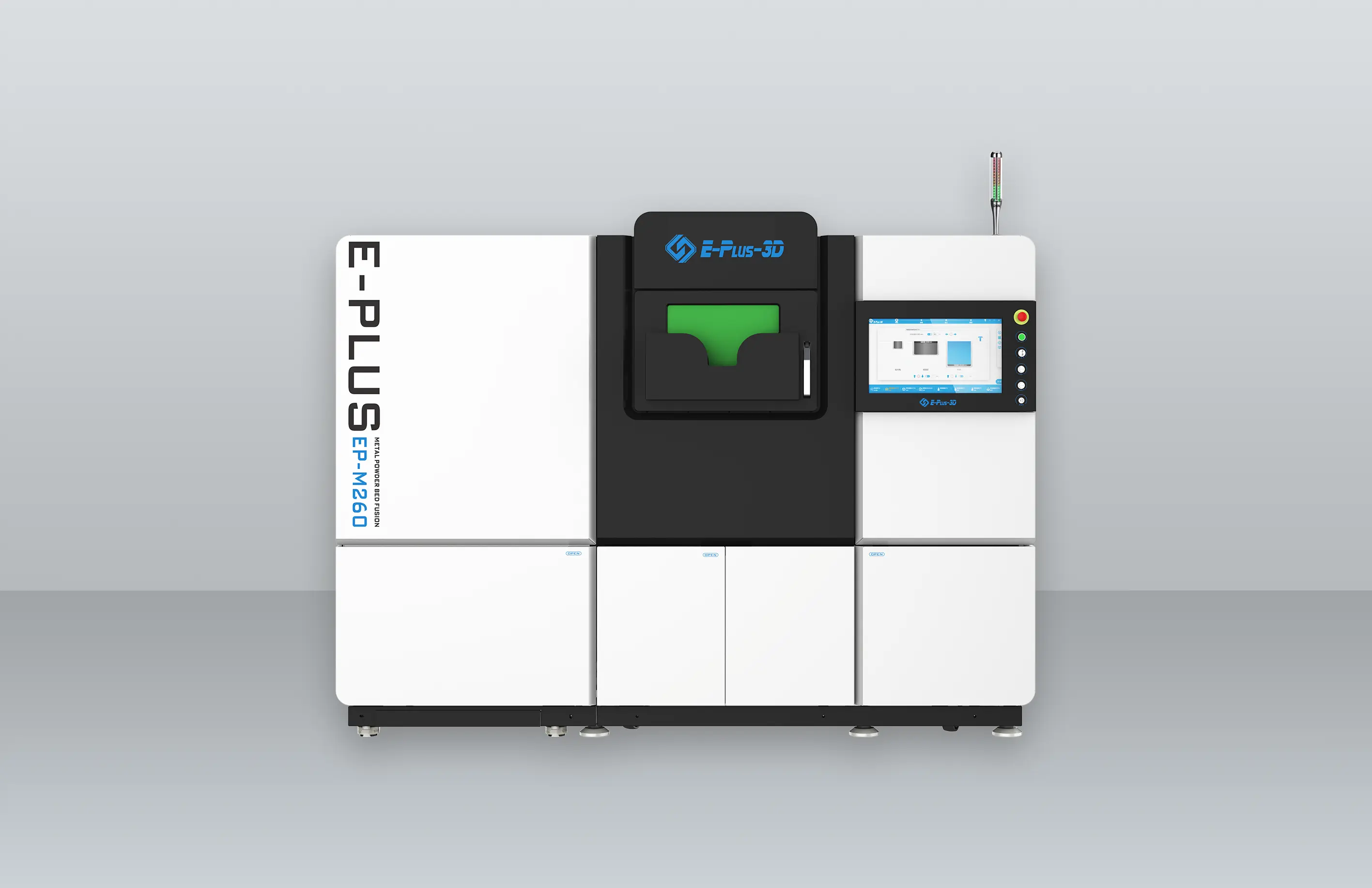
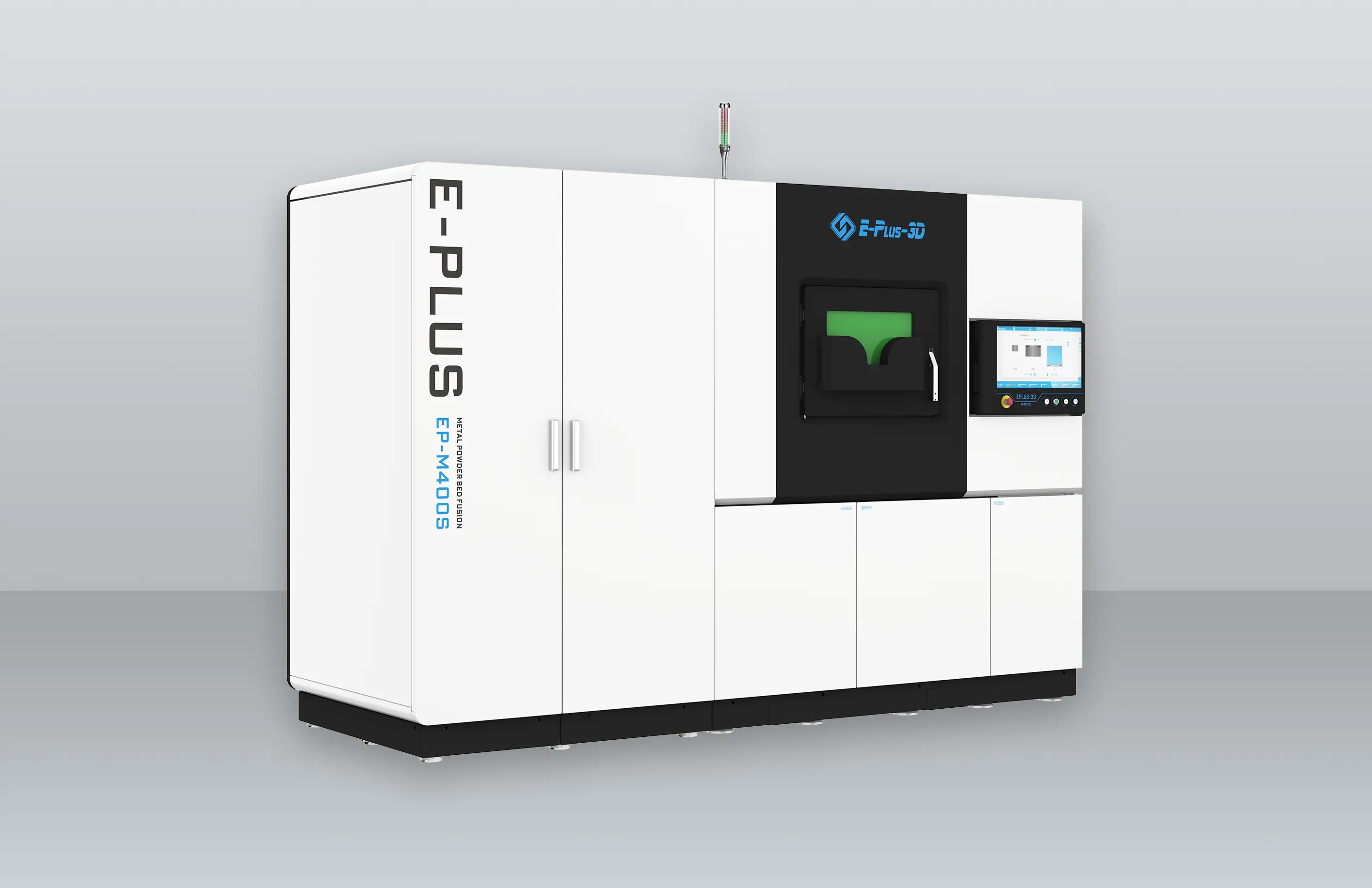
Equipment Configuration: Enabling Manufacturing from Large Structures to Precision Parts
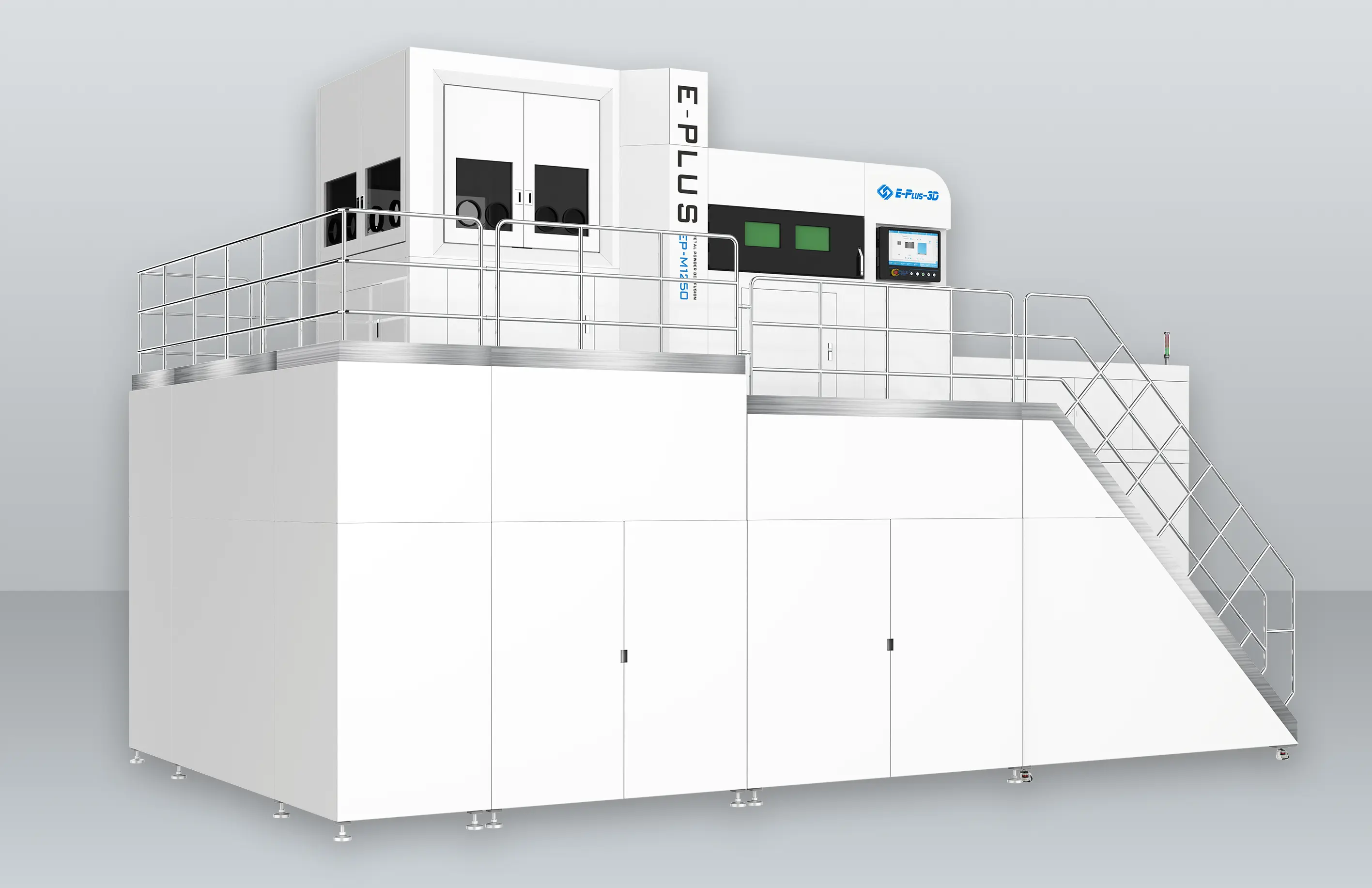
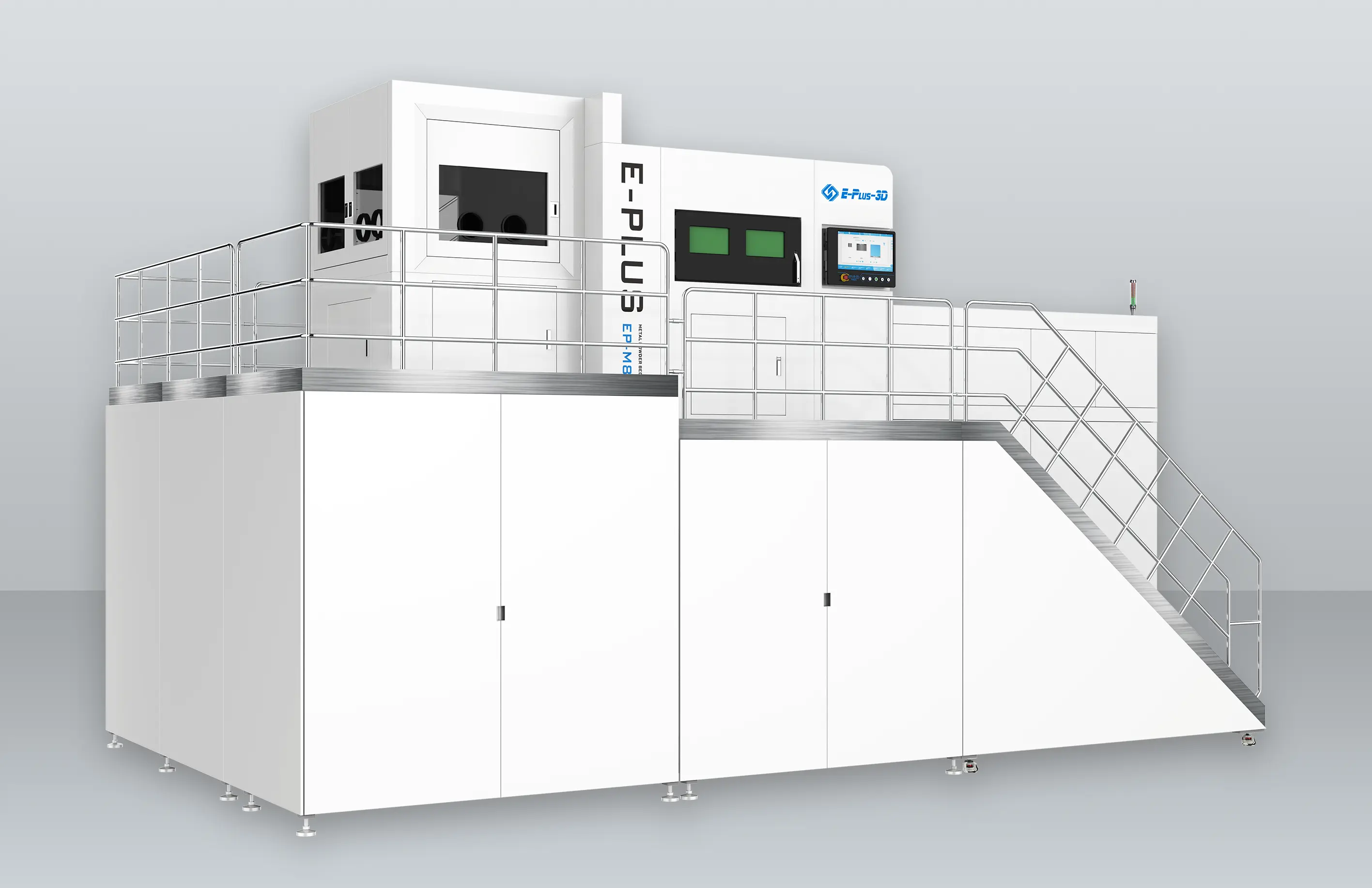
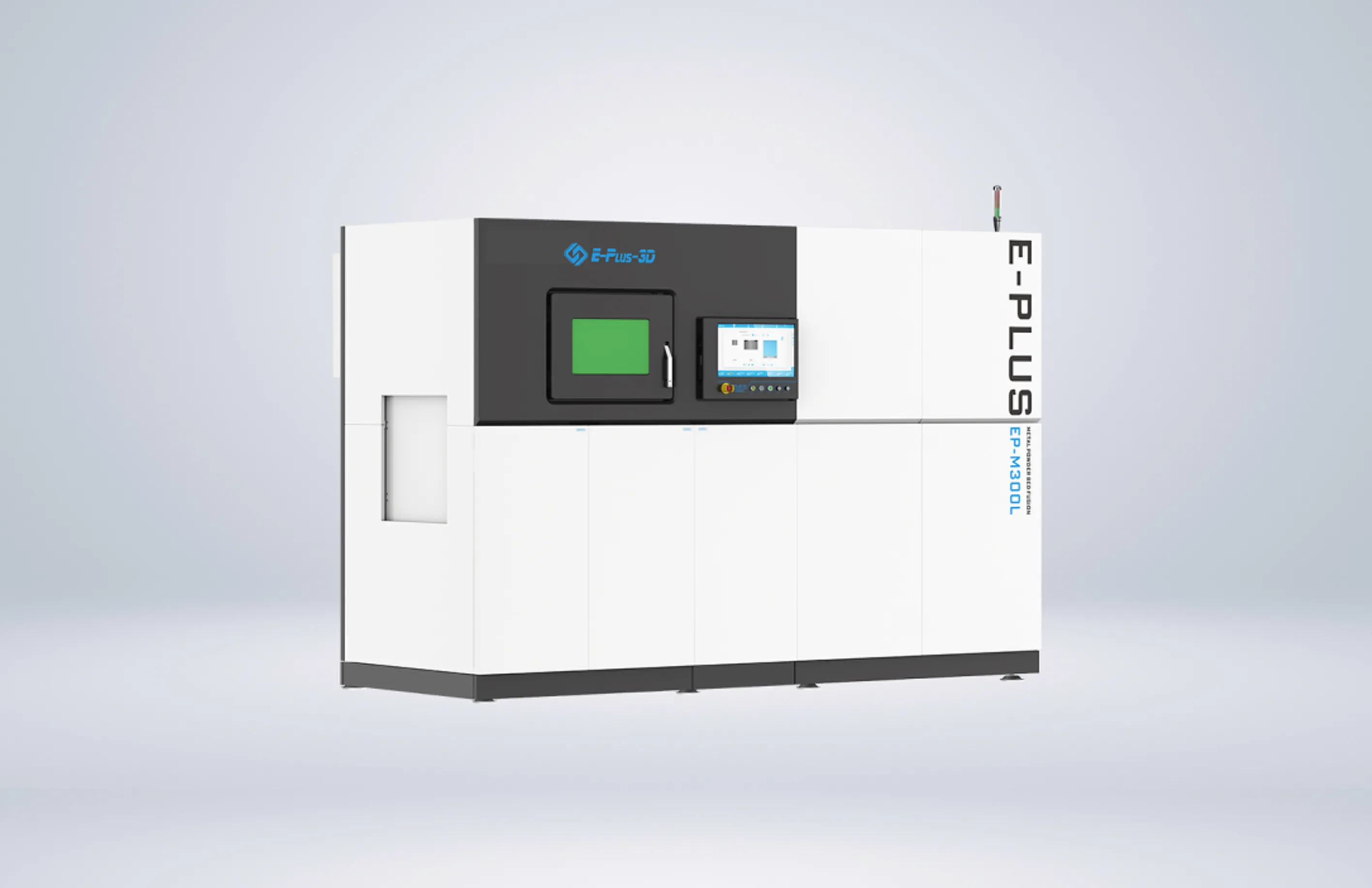
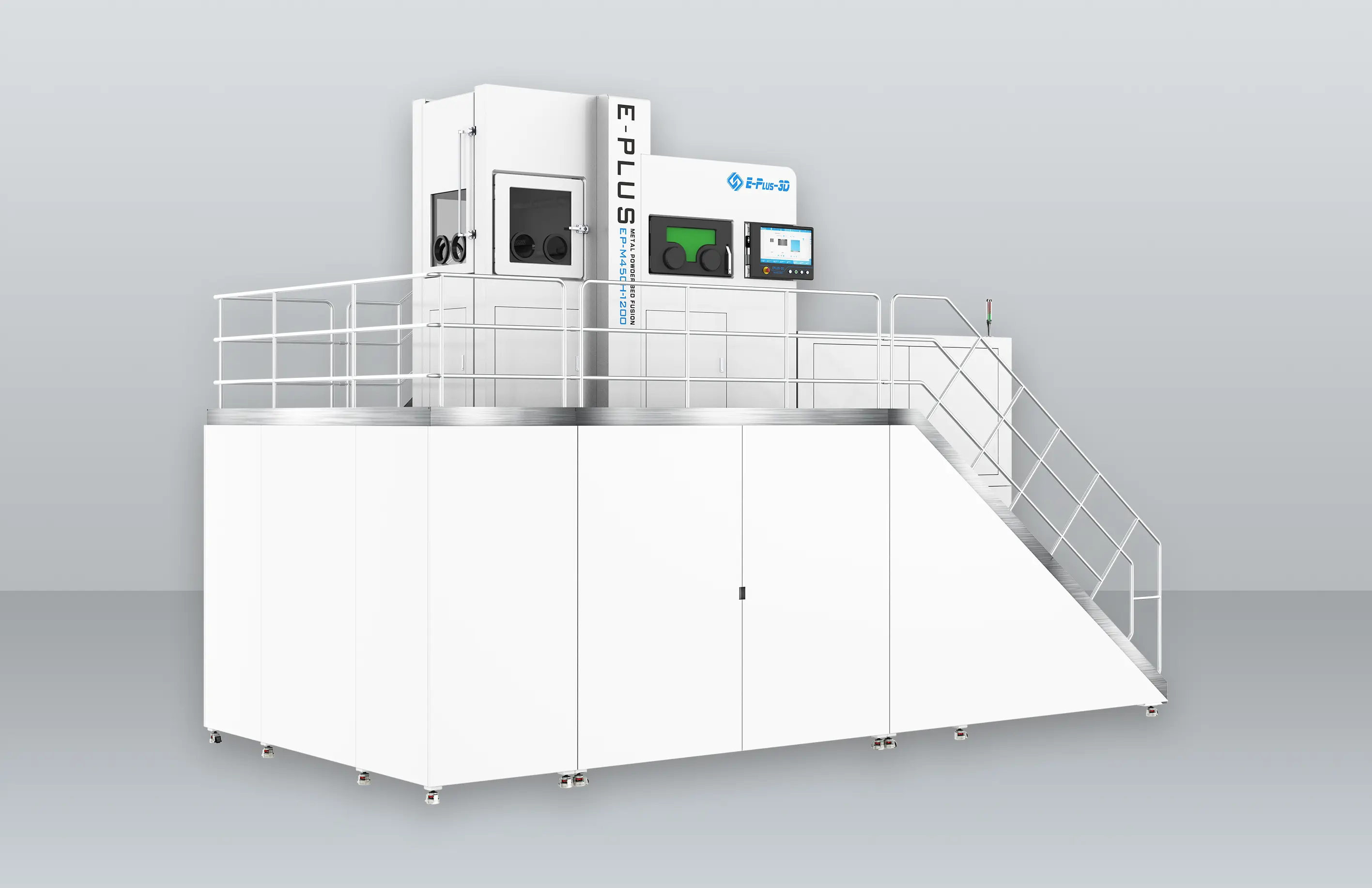
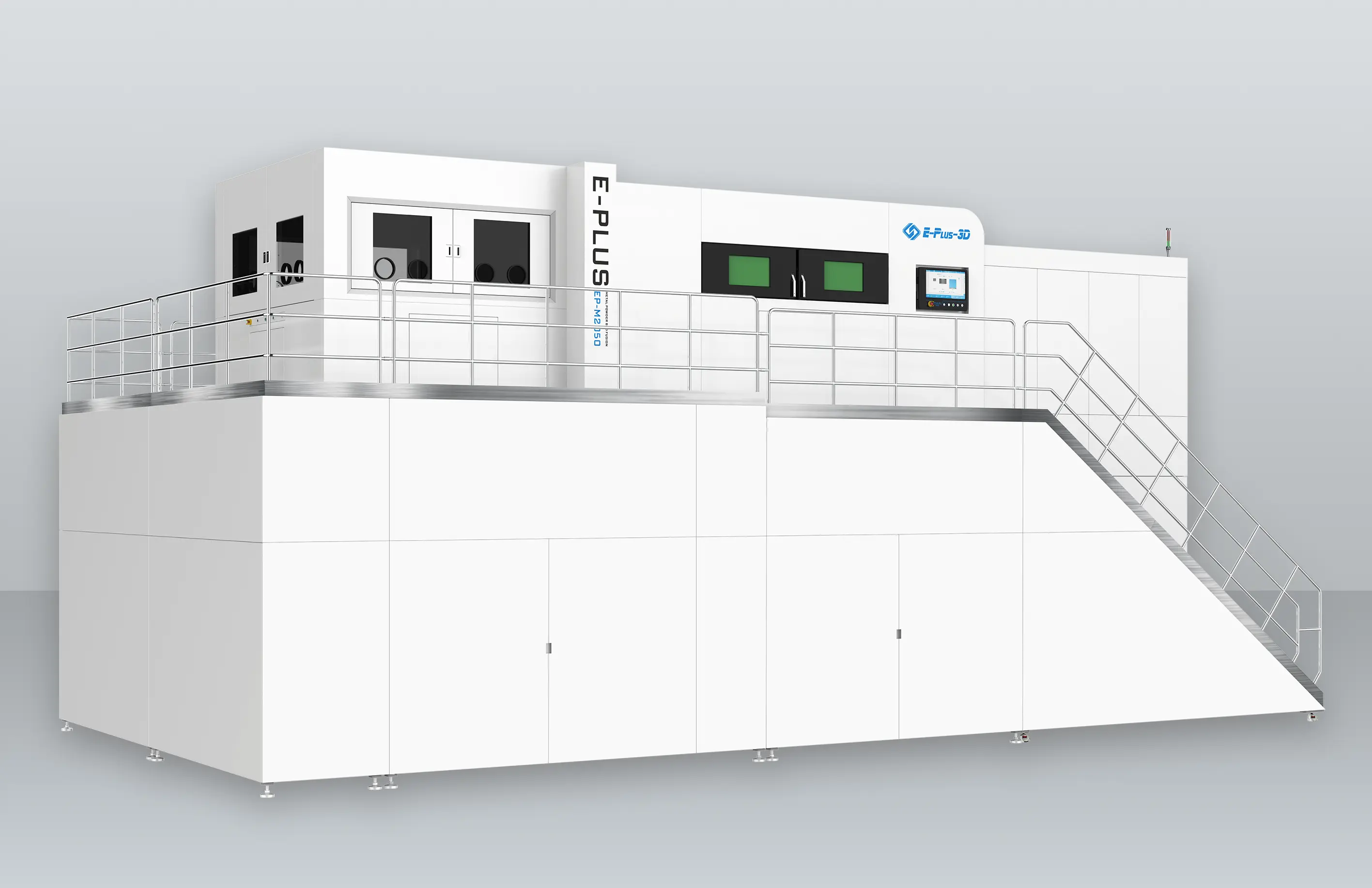
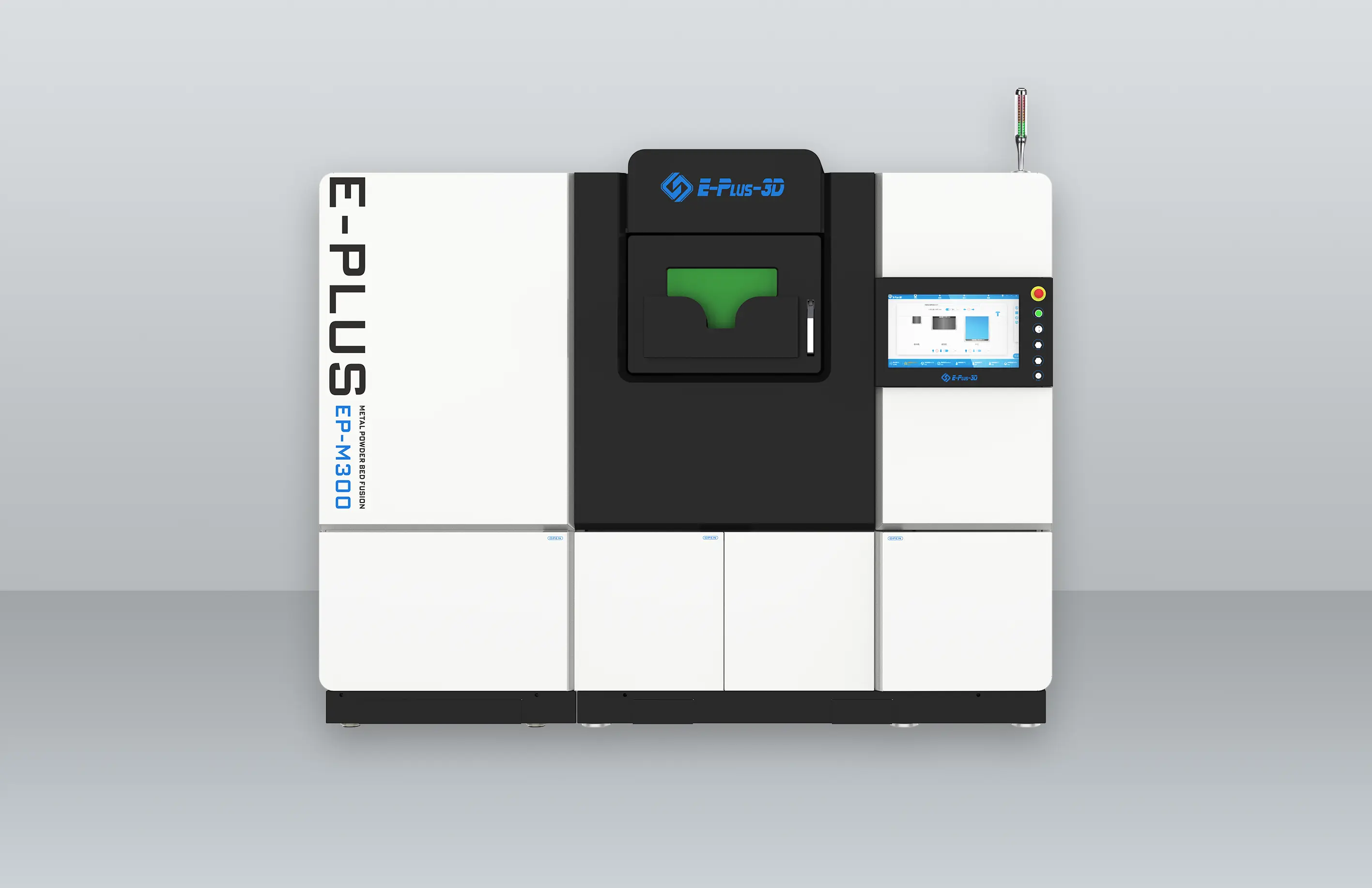
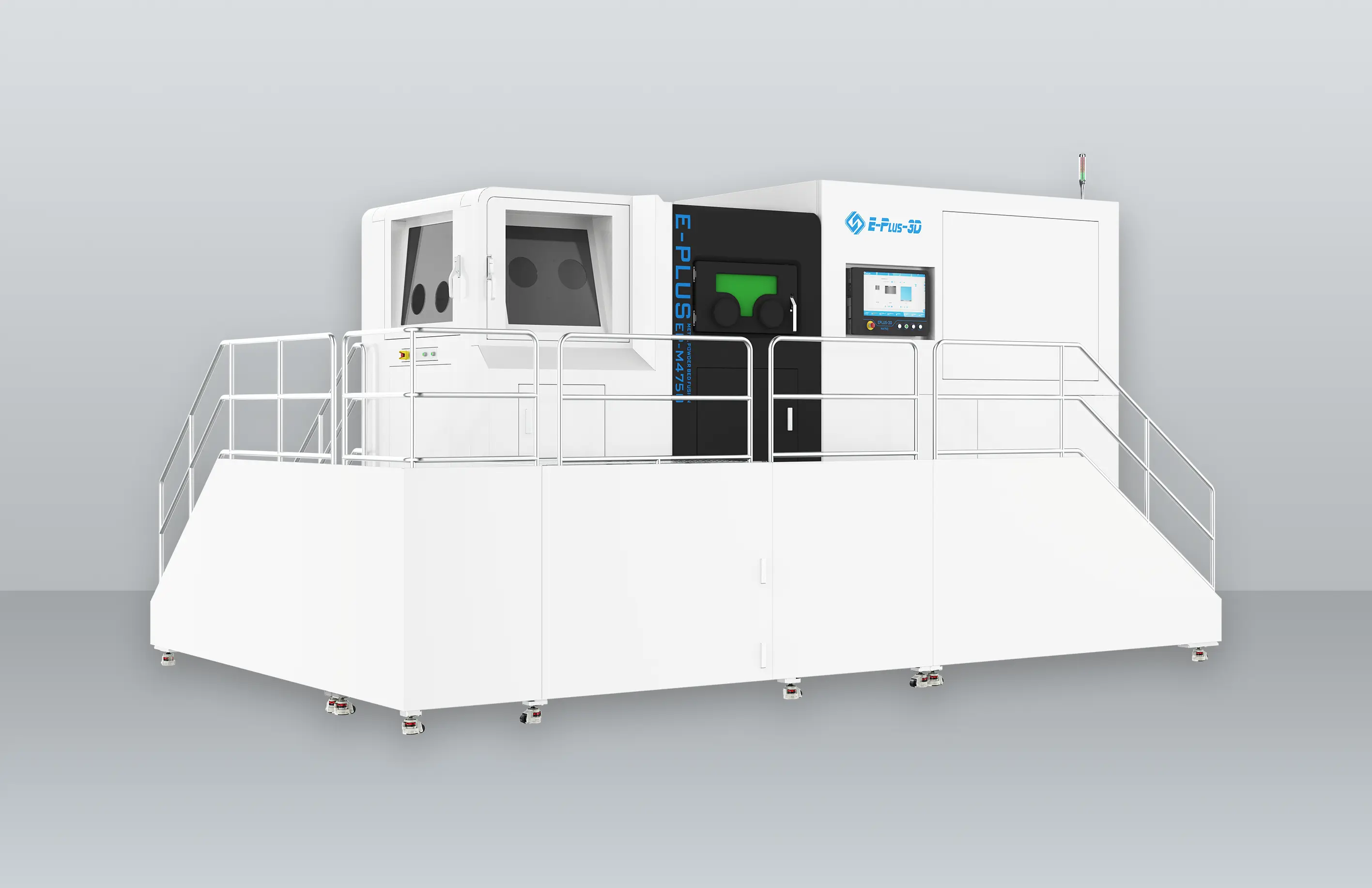
INNOSPACE has adopted three metal 3D printers from Eplus3D to establish its additive manufacturing system for aerospace applications—one large-format EP-M450 and two medium-sized EP-M300 machines. The large-format EP-M450 enables integrated printing of large structural components, making it particularly suited for the overall production of rocket parts. By minimizing multi-part assembly and welding, it enhances structural strength and production efficiency.
EP-M300 systems also excel at precision manufacturing of smaller, complex components, supporting a versatile production setup. All machines support a variety of aerospace-grade metal materials, meeting the rigorous requirements for lightweighting, high-temperature resistance, and dimensional accuracy in aerospace manufacturing.

INNOSAPCE’s Hwaseong Campus (Advanced Manufacturing Division) equipped with Eplus3D metal 3D printers
Accelerating Rocket Component Output and Reducing Costs
Following the deployment of metal 3D printers, INNOSPACE established its Advanced Manufacturing Division, dedicated to the in-house production of rocket engines and core components for space launch vehicles. By leveraging Metal Powder Bed Fusion (MPBF) technology, INNOSPACE has revolutionized its manufacturing approach—building material layer by layer only where needed. This enables on-demand production, streamlines workflows, maximizes material efficiency, and significantly reduces labor and processing costs.
Recently, INNOSPACE successfully developed and initially produced 13 key components for the HANBIT launch vehicle, including critical first- and second-stage oxidizer pumps and their high-precision rotating parts. Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, this approach is expected to reduce production costs by up to 50%, while also improving process reliability, product consistency, and shortening production lead times.
The division has officially commenced full-scale operations after verifying the reliability of its quality through Factory/Site acceptance test conducted in accordance with ISO/ASTM 52941-20. This achievement marks a significant milestone in INNOSPACE’s journey toward the serial production of rocket engines and space launch vehicle components.

Oxidizer Pumps for ‘HANBIT-Nano’ 3D printed with Eplus3D systems — First Stage (Left), Second Stage (Right)
Pioneering the Future with Metal 3D Printing
This collaboration not only enhances INNOSPACE’s commercial competitiveness but also showcases Eplus3D’s technical expertise in high-end manufacturing for global aerospace applications.
INNOSPACE has outlined three key objectives to achieve by the end of the year:
1. Stabilizing serial production of launch vehicle engines and core components through 3D printing technology,
2. Establishing a data-driven quality management system, and
3. Continuously optimizing manufacturing costs while shortening delivery lead times.
Eplus3D will continue to provide strong technical support, as both companies work together to elevate aerospace manufacturing to the next level.