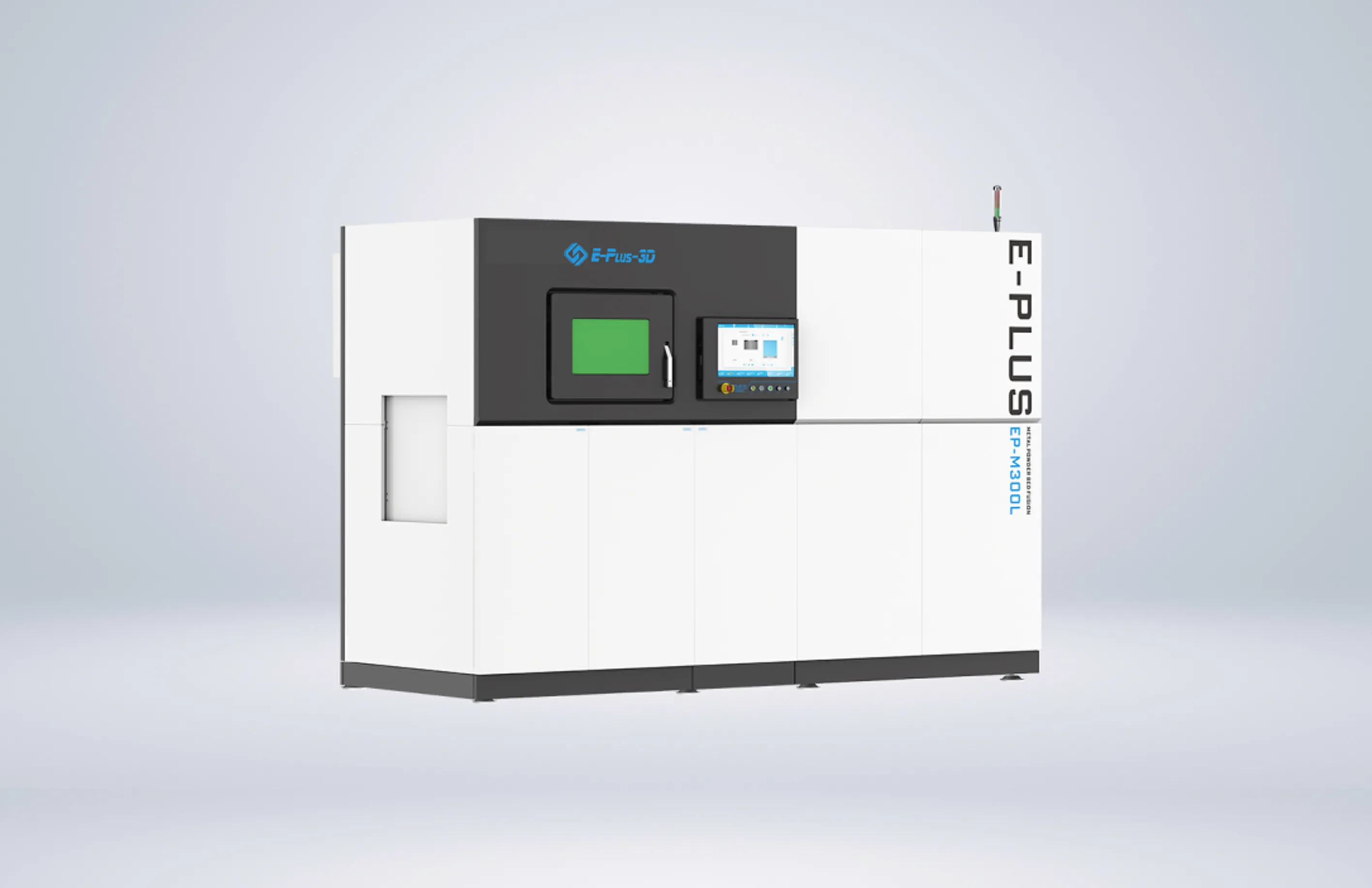
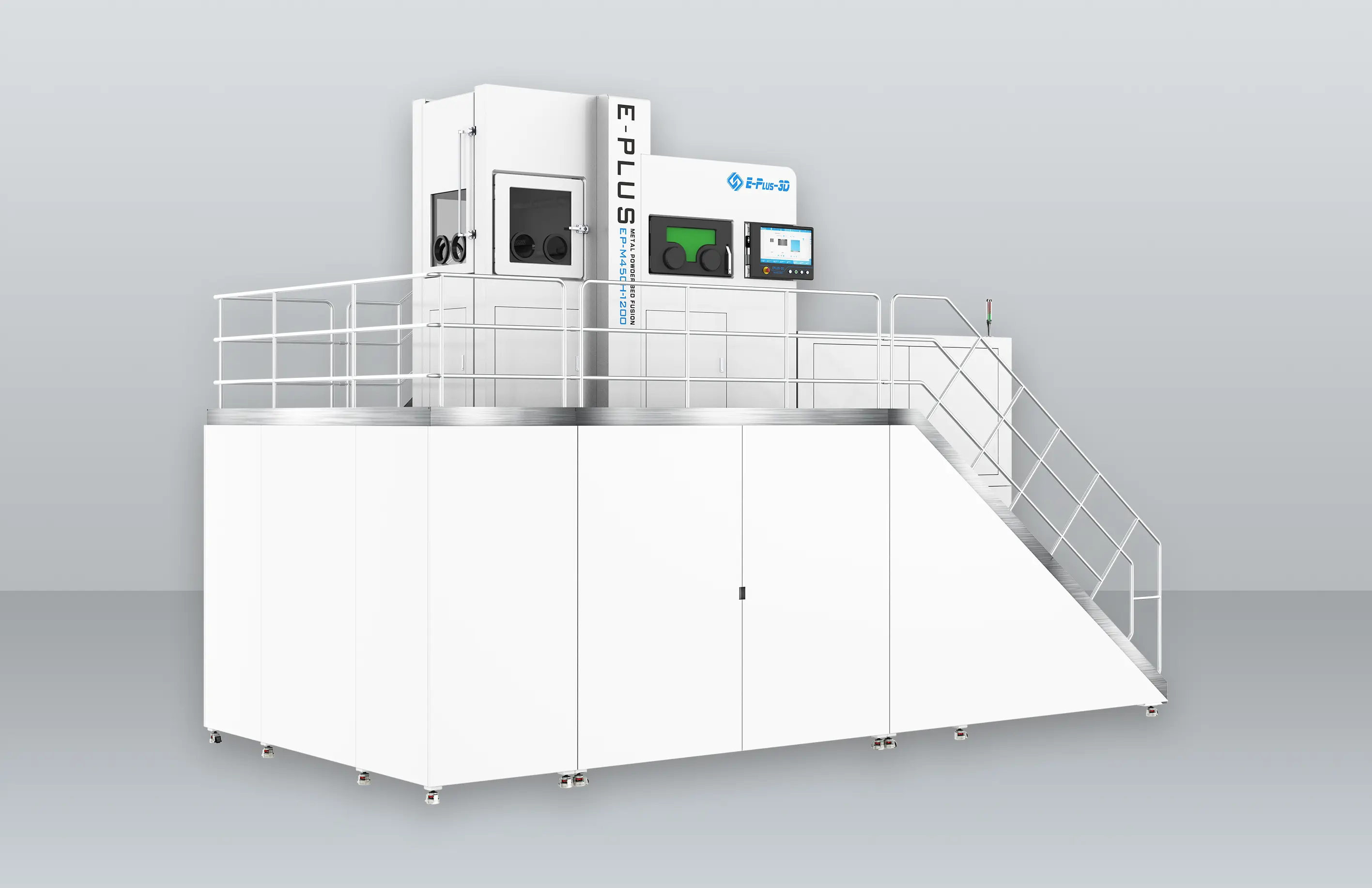
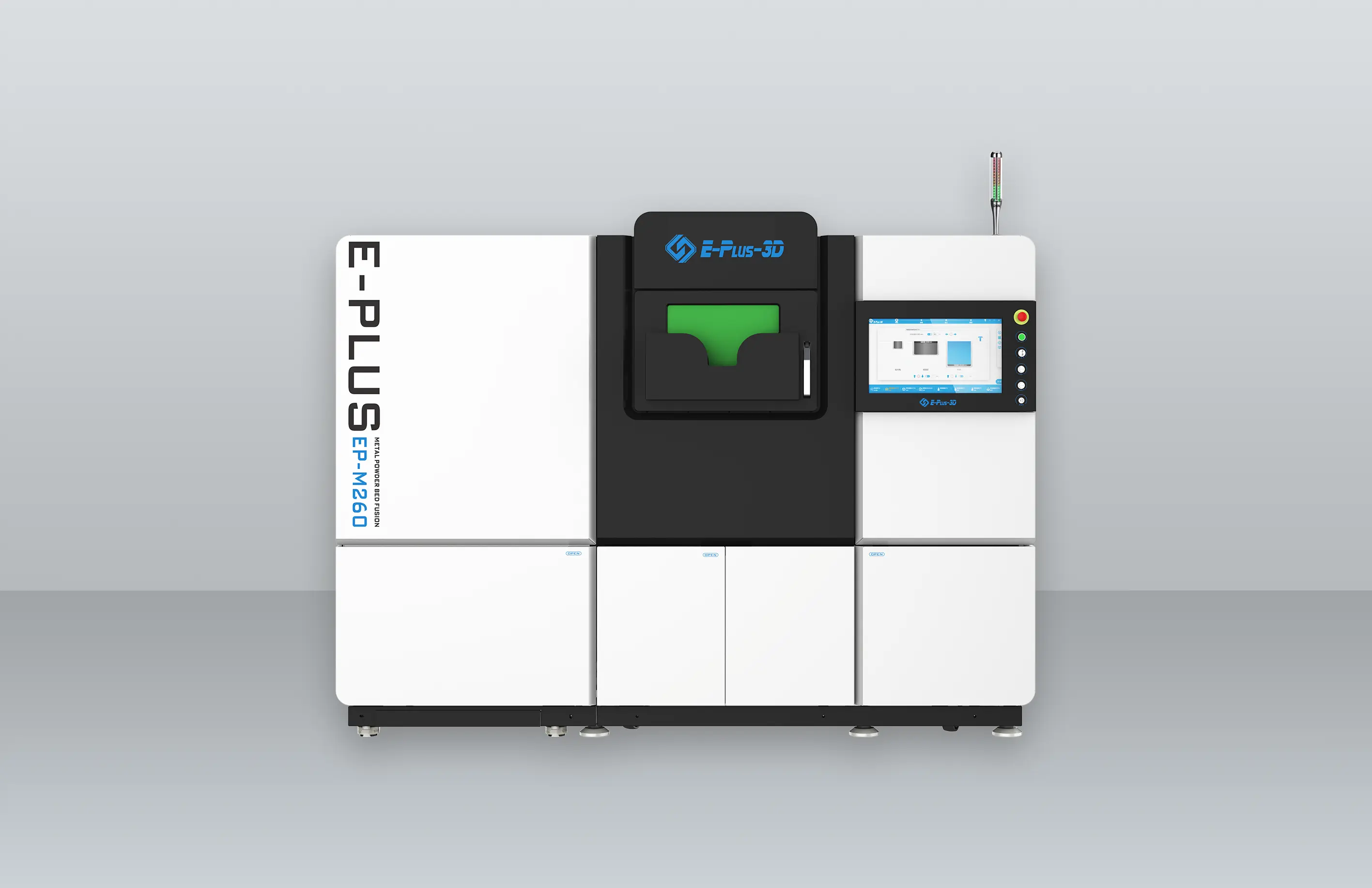
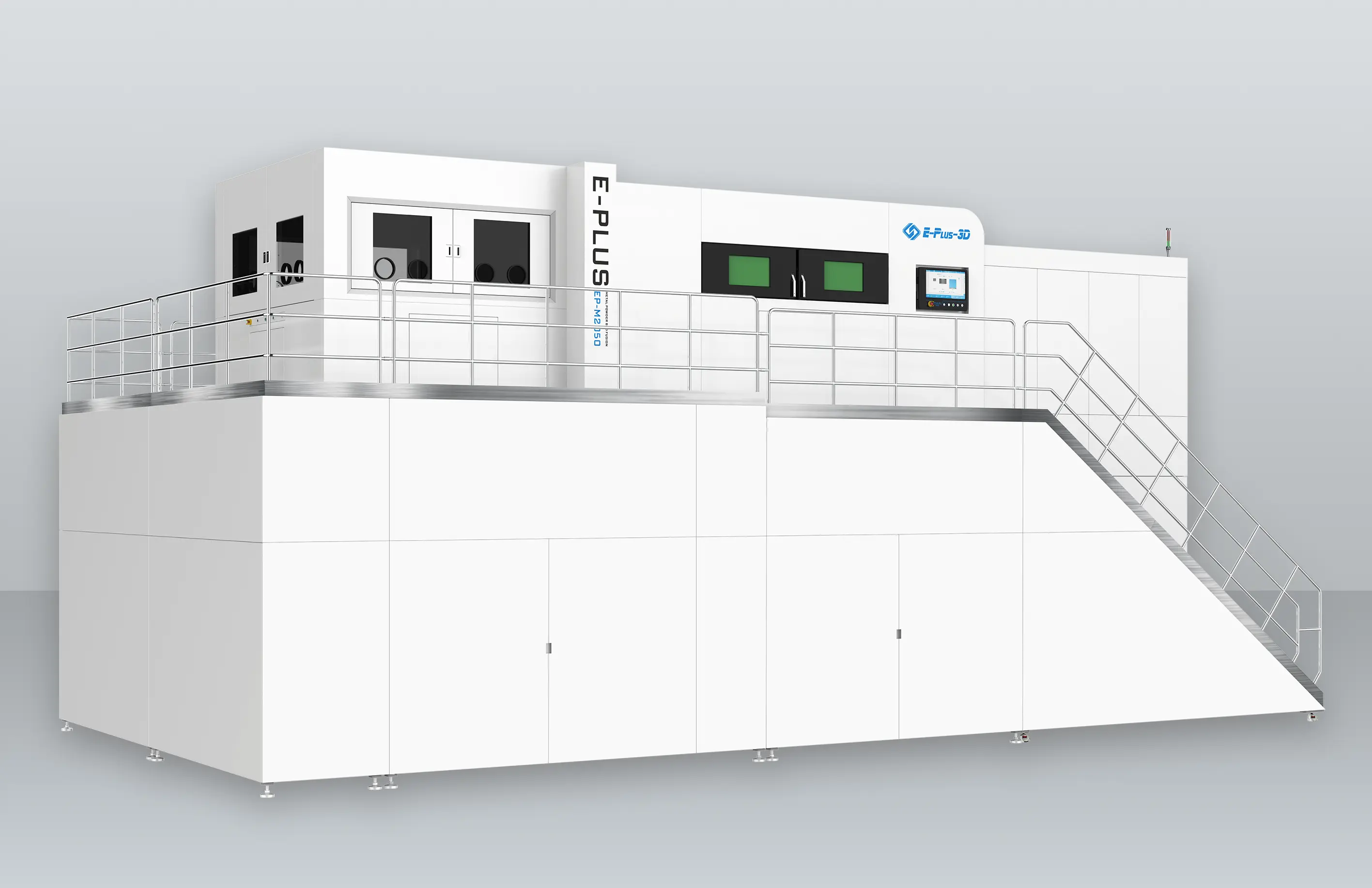
- Metal AM Machines
-
Products
Additive Manufacturing Machines Additive Manufacturing Materials Software Solutions Technical ConsultingAdditive Manufacturing Machines
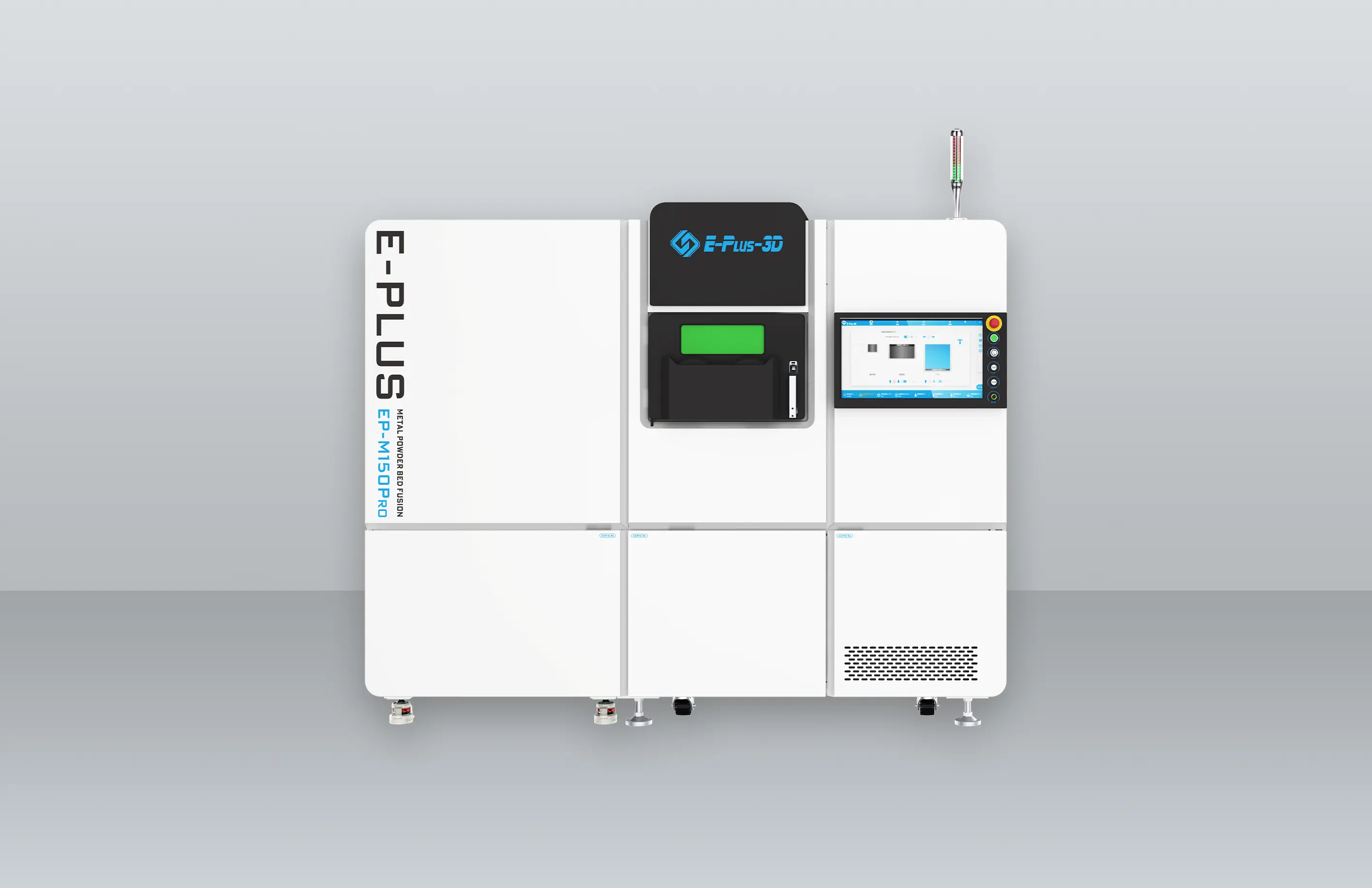
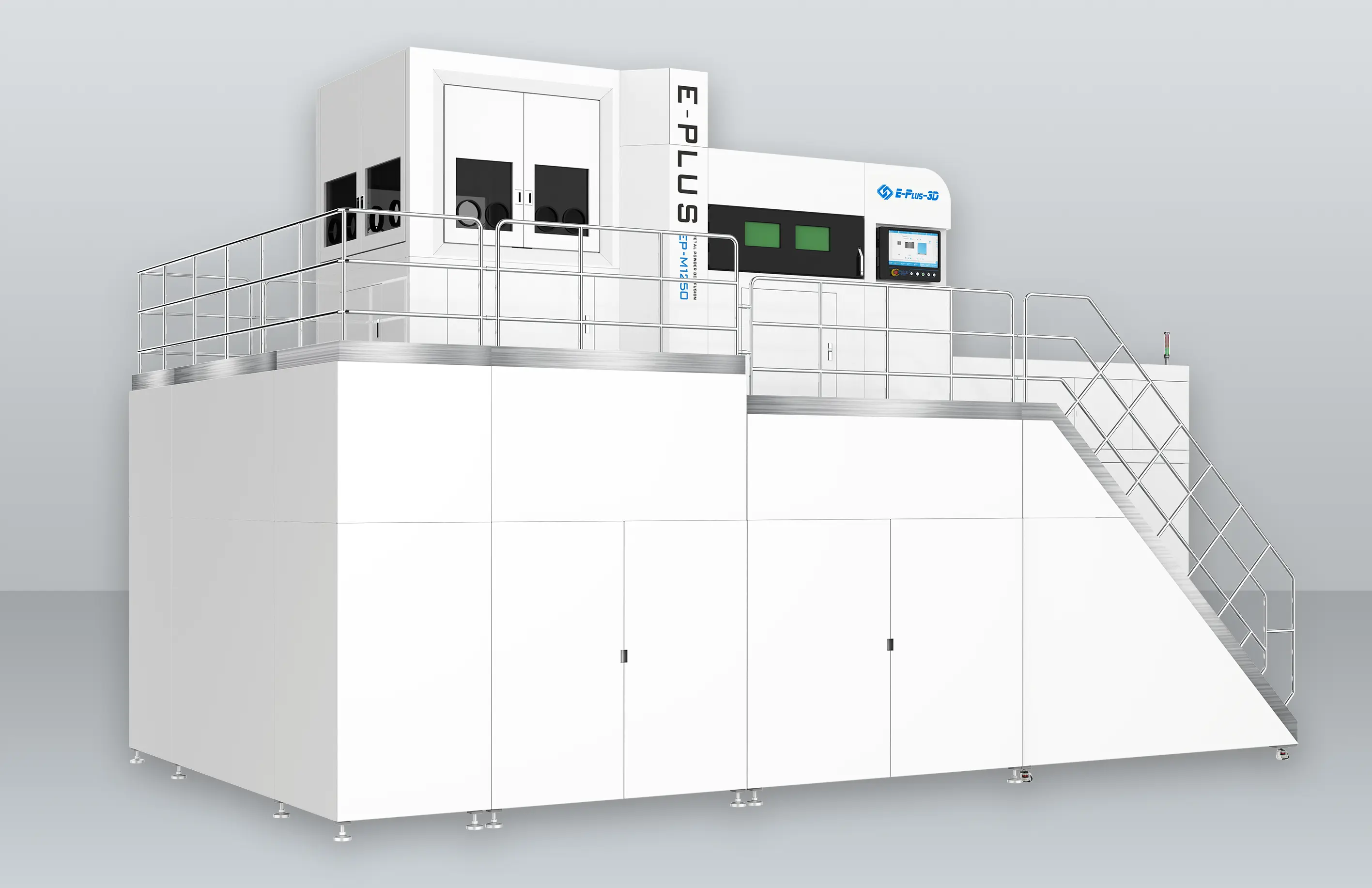
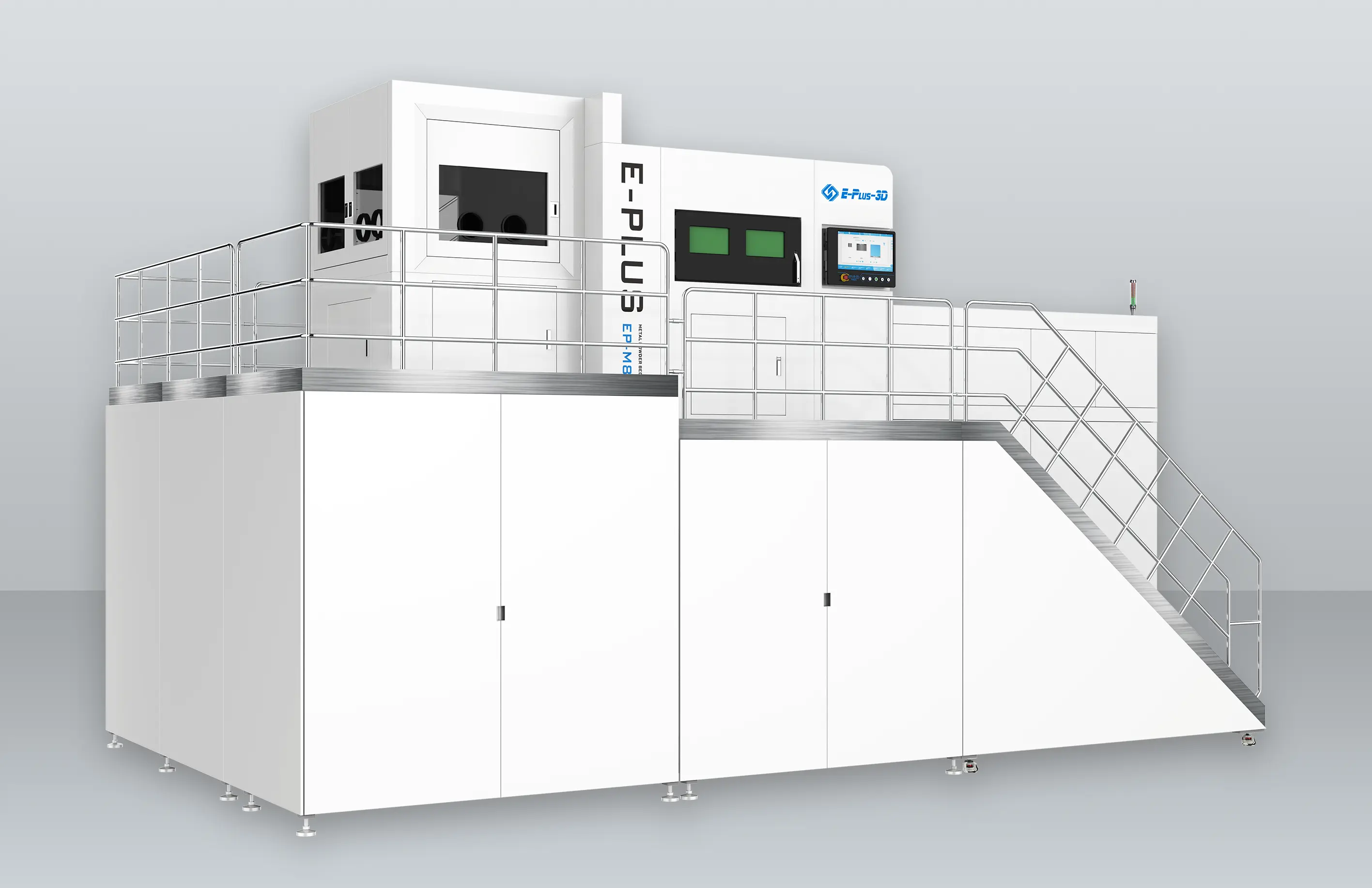
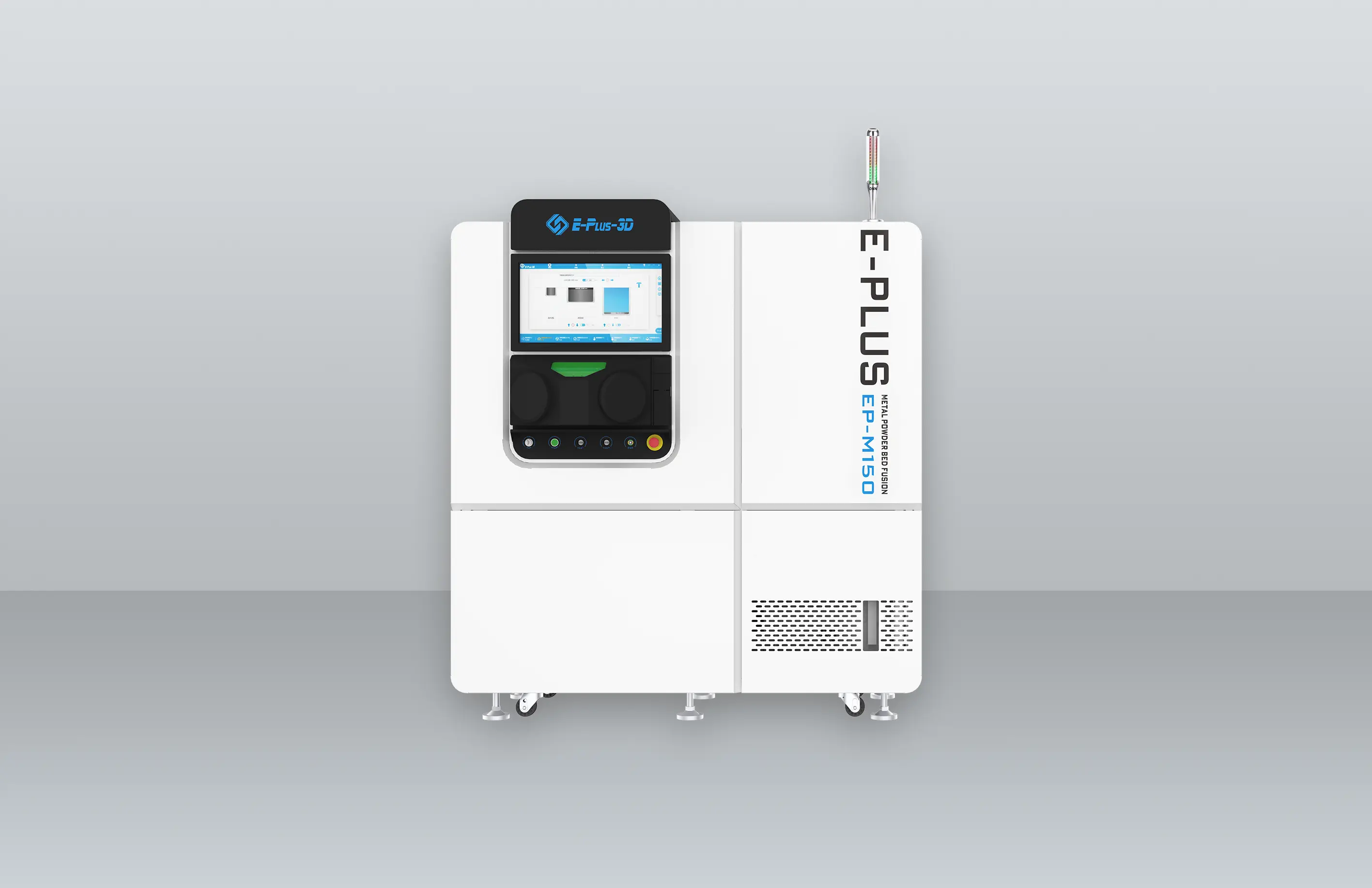
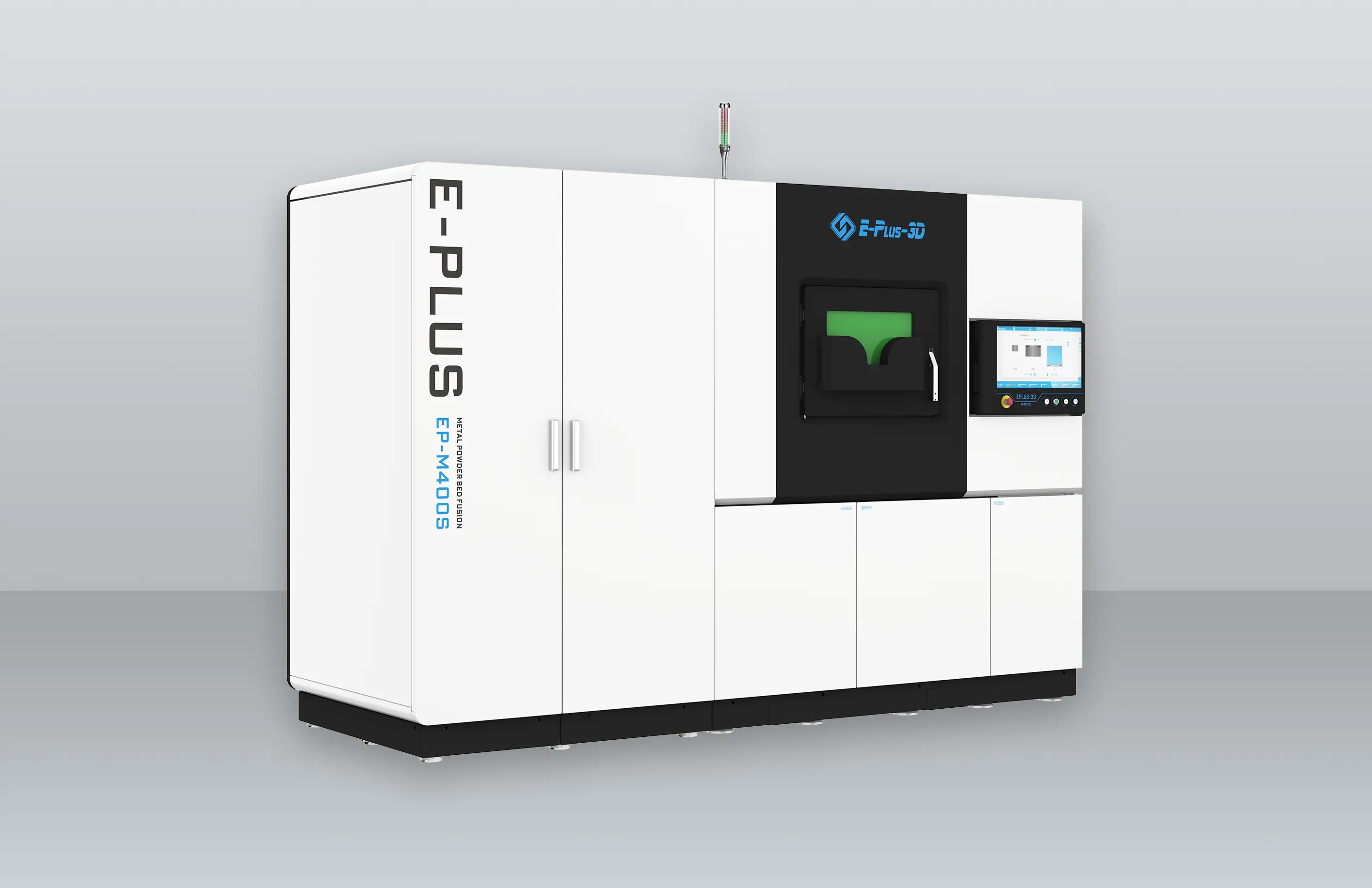
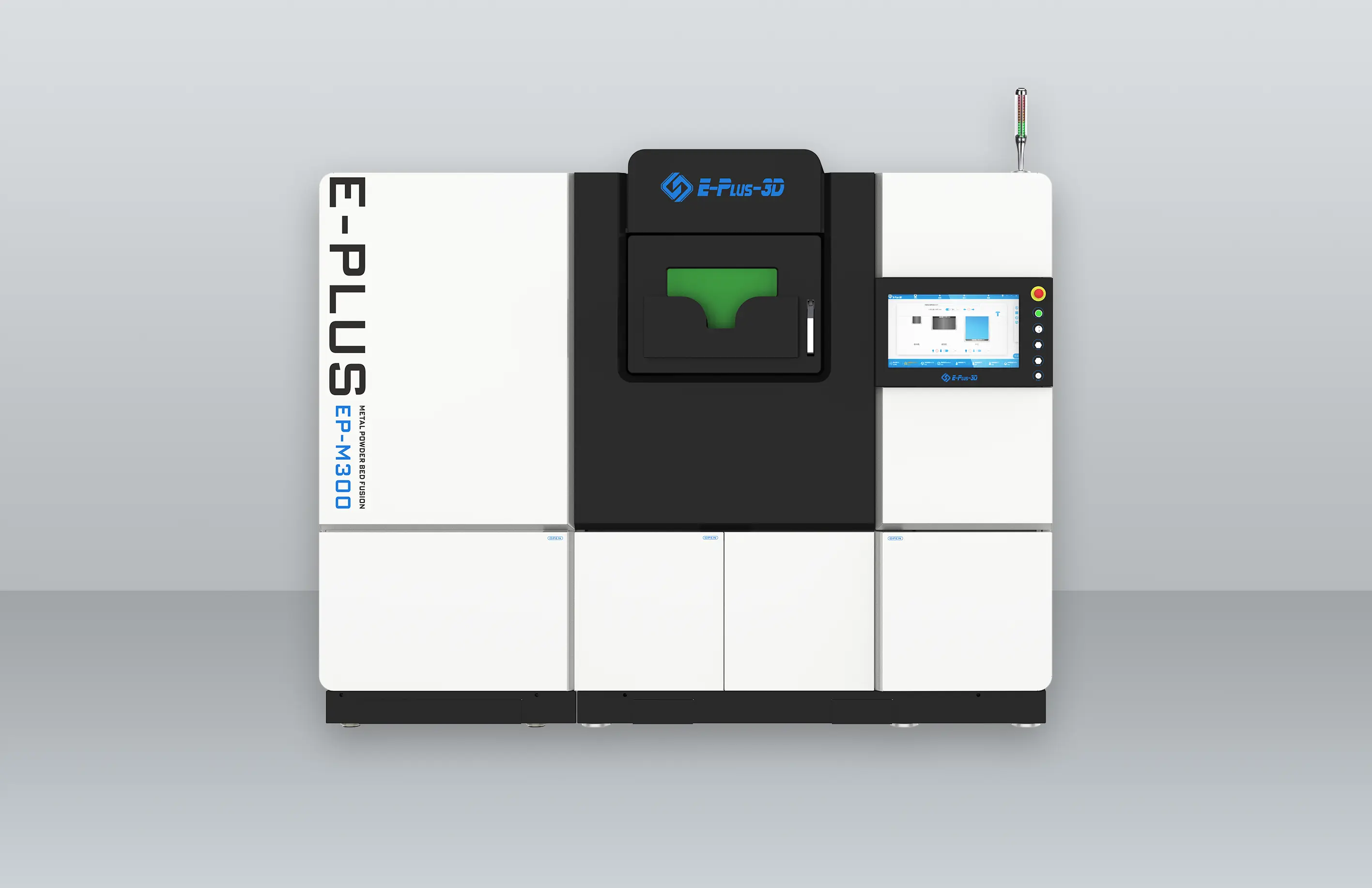
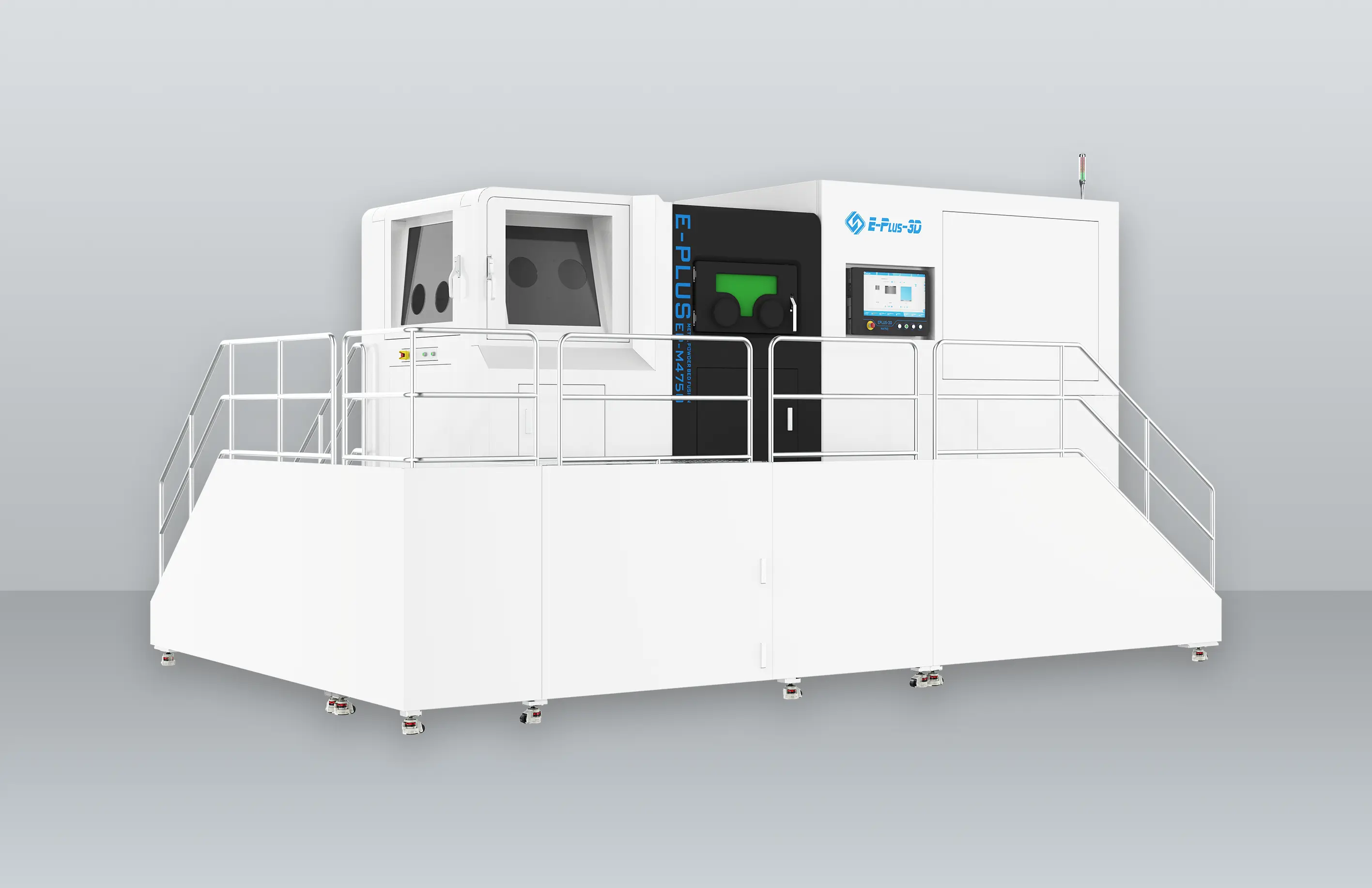
Eplus3D is a global leader in additive manufacturing (AM) solutions, specializing in high-performance metal 3D printing technologies. We empower industries - including aerospace & aviation, automotive, energy, oil & gas, machinery, tooling, healthcare, 3C products, and semiconductor manufacturing - with innovative, productivity-driven AM systems that maximize ROI, streamline production, and accelerate innovation.
Additive Manufacturing MaterialsWith the industry's advanced level of 3D printing metal, polymer, stereolithography and other additive manufacturing technologies, Eplus3D has independent research and development of laser technology-based metal and high-performance plastic additive manufacturing printing equipment and materials, which are widely applied in aerospace, automotive, medical, mold industries, etc.
Software SolutionsThe software solution independently developed by Eplus3D is easy to operate with the features of one-click printing, offline analysis, etc., which can maximize printing efficiency and reduce labor costs. This is also one of the core competitiveness of Eplus3D in the metal 3D printing process and additive manufacturing system.
- Industries
- Resources
- About
- Support